Skin diseases are very common in dogs and the condition of a dog’s skin is normally indicative of its health. Skin disorders in dogs is normally manifested in changes in your dog’s coat and development of papules, pustules, scaling, discolored skin, redness, hair loss, dandruff, and skin sores.
There are several ways to treat dogs with skin diseases such as: antibiotics, antifungal medications, antihistamines, corticosteroids, other anti-inflammatory drugs, topical creams, and shampoo therapy. Vitamin supplements with omega3 fatty acids can also support your dog’s health.
Vitamins are important nutrients that can contribute to the health of your dog’s coat. Vitamin A is primarily responsible for maintaining the skin’s health, and Vitamin E, which is an important antioxidant that neutralizes free radicals that accumulate in highly proliferative cells like skin and prevent the deterioration of fibrous tissue caused by these ionized molecules. Vitamin B is also essential and deficient riboflavin (B2) in your dog’s diet can lead to cracked and brittle skin. Biotin (B7) is another type of Vitamin B, and when deficient can lead to alopecia (a common disorder in dogs which causes the animal to have partial or complete hair loss).
In addition to vitamins, minerals are important to the health of your dog’s skin. The diet of your dog should be rich in minerals such as: Selenium, which is an essential nutrient that neutralize free radicals, Zinc, that plays a crucial role in protein synthesis which aids in maintaining elasticity of the skin, and Copper, which is involved in multiple enzymatic pathways. In dogs, a deficiency in copper results in incomplete keratinization leading to dry skin and hypopigmentation.
Top 10 Dog Skin Conditions and the Possible Ways to Treat Them
1) Ringworm
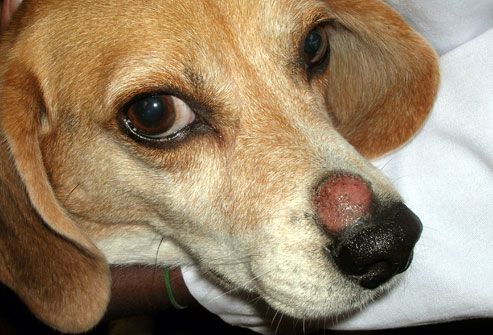
Ringworm is a skin infection caused by fungus and can be transmitted from dogs to people. Despite its name, it is not a worm. The”ring”in ringworm refers to the red, rounded patches that appear with the infection.
Symptoms of Ringworm in dogs: The infection appears as a scaly skin with hairless circular patches.
Possible Treatment: for Ringworm in Dogs
One possible treatment is the use of a topical solution to prevent fungus from spreading and oral antifungal drugs. An antifungal shampoo is also essential.
You must clean and sanitize all furniture, bedding, combs, and bowls to get rid of the fungal spores.
2) Yeast Infections
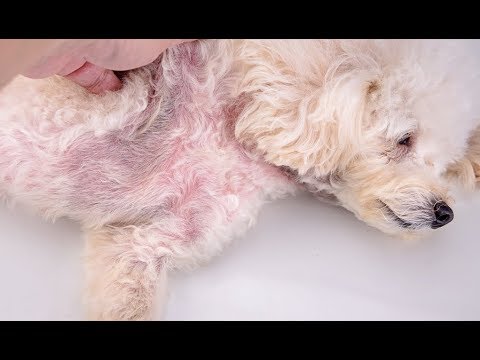
Is your dog biting its body? Does it smell unpleasant? Your dog may have a yeast infection.
Yeast infections prefer to grow in warm, moist, closed areas on a dog’s body such as: ear canals, between paw pads and between the dog’s toe, groin and perineum.
Symptoms: Yeast infections can discolor the skin and cause bad odor from infected areas.
Possible Treatment
To treat the infected areas, you can use antifungal medication, shampoos, and topical creams.
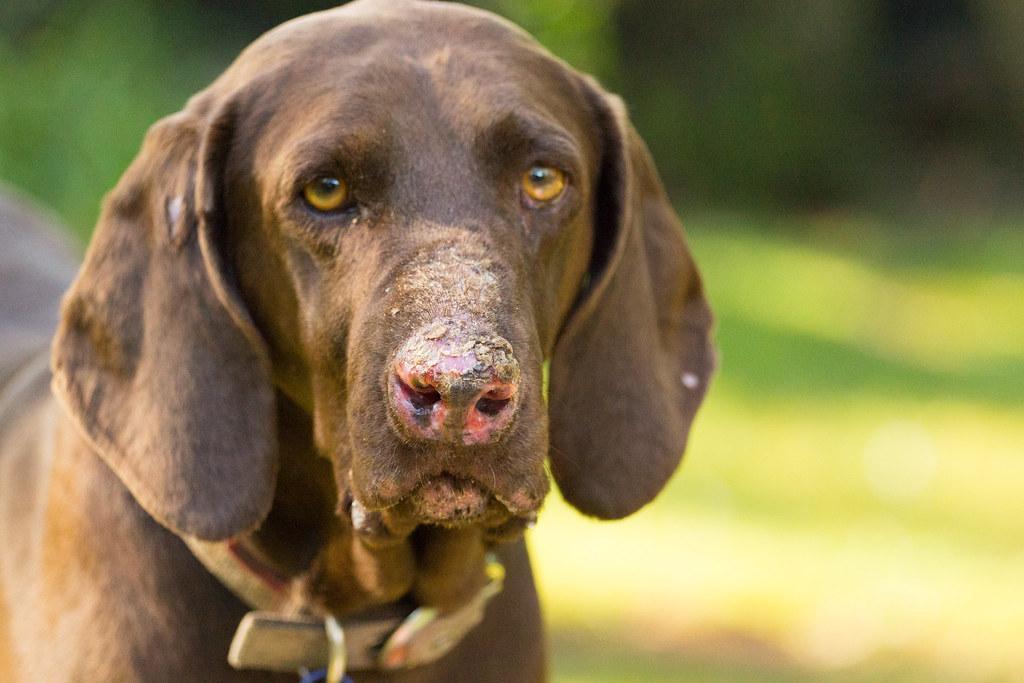
3) Skin Tumors

Like humans, dogs can develop skin tumors, especially dogs with short hair. Your dog’s skin is exposed to a myriad of environmental factors that can cause tumors such as: exposure to solar radiation, chemicals in the environment and specific types of viruses. Dogs’ coats protect them from the harmful rays of the sun so that dogs don’t develop skin cancer due to the destructive damage that would be caused by the sun.
Symptoms: If you observe a strange lump on your dog’s body, you must visit your veterinarian to determine the right treatment after performing a biopsy. In a biopsy, your veterinarian will take a sample of tumor cells to diagnose the type of the tumor (cancerous or benign).
Possible Treatments for Skin Tumors in Dogs
Examine your dog daily, and consult your veterinarian if you notice anything suspicious. Some skin tumors can be removed surgically. Other cases may require radiation or chemotherapy.
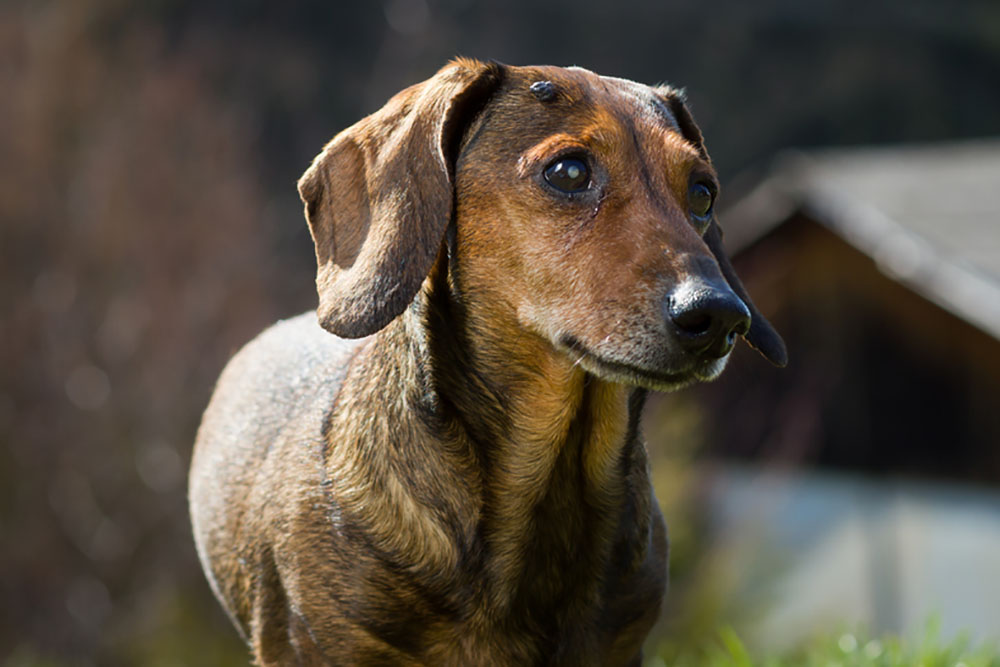
4) Lupus

Lupus is an autoimmune skin disease in which the immune cells attack the body’s own cells. There are two types of lupus: Discoid Lupus Erythematosus (DLE) and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE). Discoid Lupus Erythematosus (DLE), also known as nasal solar dermatitis, affects the skin around the nose, lips, and mouth. There are many factors that can lead to lupus including: genetic factors, viral infection, some medications, and ultraviolet light.
Symptoms of Lupus in Dogs: Discoid Lupus Erythematosus (DLE) is indicated by redness of the skin, especially the nose, lips, and face, sores or ulcers and scratching at affected areas.
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) affects any area of the body. Indicators of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) are fever, hair loss, loss of appetite, and anemia.
Possible Treatments for Lupus in Dogs
The Treatment for lupus depends on its type. DLE is treated with topical and oral steroids (Prednisone), given that steroids suppress the immune response and reduce irritation.
SLE treatments depends on the affected organs. Immunosuppressive drugs, or steroids, for instance, Prednisone may be used to fight against lupus. Chemotherapy is also an important method to suppress the negative immune response.
5) Mange
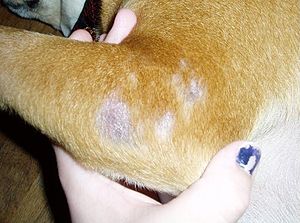
Mange is a skin disorder that can be caused by several parasitic mites. There are two types of mange: Demodectic mange and Sarcoptic mange. Demodectic mange (known as red mange or demodex) is caused by Demodex canis mites. Sarcoptic mange (known as scabies) is caused by Sarcoptes scabiei mites.
Symptoms of Mange in Dogs: Sarcoptic mange is a contagious disease that can be transmitted to other dogs and even people. Affected dogs scratch endlessly which results in bald patches, redness, rashes, and scabs. It typically starts on the face, ear, and legs, but may spread over the entire body. Demodectic mange can cause bald spots, scabs, and sores. On the other hand, Demodectic mange affects dogs under one year old.
Possible Treatments for Mange in Dogs
Topical medications and medicated shampoos are used for treatment of mange.
6) Pyoderma

Pyoderma is a bacterial skin infection. Pyoderma occurs when skin is injured or cut. This is normally caused by a bite wound, chemotherapy, poor diet, mites, and environmental factors. There are two types of pyoderma: Superficial pyoderma and Deep pyoderma.
Symptoms of Pyoderma in Dogs: Signs of pyoderma are lesions, pustules, redness, and hair loss.
In Superficial Pyoderma, the skin disorder appears on the outer layers of your dog’s skin.
Whilst in Deep pyoderma, the infection occurs in cuts on inner areas of the skin.
Possible Treatments for Pyoderma in Dogs
Cases of pyoderma are treated with oral antibiotics and/or topical antibacterial therapy.
7) Folliculitis
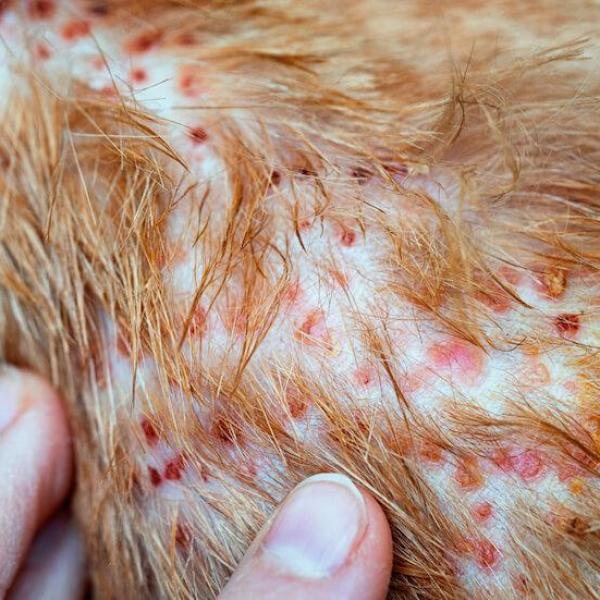
Folliculitis is characterized by inflamed hair follicles which are caused by bacteria or yeast getting into the follicle.
Symptoms of Folliculitis in Dogs: Indicators of Folliculitis include: redness, swelling, hair loss, bumps, and sores on the skin’s surfaces.
Possible Treatments for Folliculitis in Dogs
Topical antibacterial ointments and antimicrobial shampoos are used for treatment. It should be noted that the shampoo should be applied to the dog’s skin at least 10 minutes before washing off in order to be effective. If your dog’s case is advanced, antibiotics can be used to assist with your dog’s health improvement.
8) Seborrhea
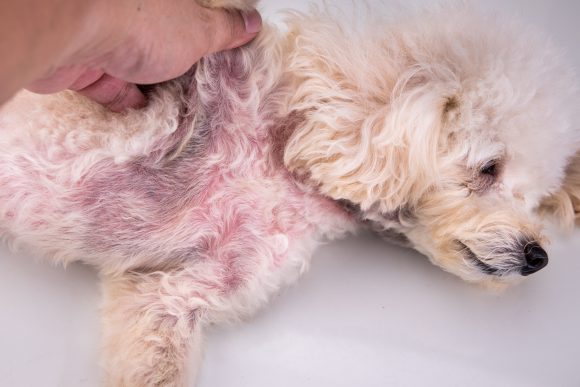
Seborrhea, also known as Seborrheic Dermatitis, is a skin disorder that causes skin flaking and peeling. Seborrhea develops because of medical conditions, allergies, hormonal imbalance, environmental factors such as: temperature, humidity changes and dietary imbalance- poor diets containing low levels of omega-3 fatty acids. There are two common types of Seborrhea: Seborrhea Sicca (dry seborrhea) and Seborrhea Oleosa (oily seborrhea). Most dog cases with Seborrhea have a combination of dry and oily seborrhea.
Symptoms of Seborrhea in Dogs: Symptoms of Seborrhea are a yellow or red rash, flakiness and itchiness of the dog’s skin.
Possible Treatments for Seborrhea in Dogs
Cases of Seborrhea are treated with antibiotics, corticosteroids (e.g., prednisone), omega-3 fatty acid supplements, topical spray and medicated shampoo.
9) Allergic Reactions

Allergic reactions are a very common problem that can affect a dog’s skin. An allergic reaction can be triggered by the environment, the food it consumes, ticks, and fleas. Environmental allergies (Atopy) causes irritation of the dog’s skin. It can be triggered by grass, ragweed, dirt, and pollens. Like humans, some dogs can develop an allergic response to some types of food, such as protein: beef, chicken, eggs, chicken, and dairy. Ticks and fleas can also cause irritation and inflammation.
Symptoms of Allergic Reactions in Dogs:
Environmental allergies appear as red, swollen, inflamed areas of the skin and rashes.
Food allergies symptoms normally manifest as vigorous itching by your dog which may break the skin. The saliva of ticks and fleas can induce an allergic response that causes irritation, rashes, and red-hot spots.
Possible Treatments for Allergic Reactions in Dogs
To treat Environmental allergies (Atopy) Corticosteroids can be used.
For food allergies, the best way to diagnose a food allergy is through a food elimination for 8-12 weeks to help to determine the causes of the allergy. Once identify the allergic ingredient, supply food without that ingredient, and this should improve your dog’s health.
Tick and fleas can live in carpets and bedding, therefore you ensure should that you clean on a regular basis. You can get rid of these parasites by using medicated shampoos, ointments, and pills. You can further apply topical creams and oral antihistamines to treat skin inflammation.
10) Dandruff

Dogs can get dandruff and dry skin like humans. Dandruff is the presence of dead skin cells on your dog’s coat.
Symptoms of Dandruff in Dogs: Dandruff normally represents a sign of a hidden problem, such as an infection. Also, poor nutrition in winter can cause extremely dry skin.
Possible Treatments for Dandruff in Dogs
A high-quality source of protein, omega 3 and 6 fatty acids can keep the dog’s coat healthy. Simple cases of dandruff are easy to treat with dandruff shampoos.
Here are 5 Ways to Take Care of your Dog’s Skin and Coat
- Groom your dog regularly
- Eliminate external causes of irritation, including fleas, mites, and other parasites
- Examine your dog daily, and consult your veterinarian if you notice anything suspicious.
- Ensure that your furry companion drink adequate water. This keeps your dog dehydrated and provides nourishment to the skin.
- Supplement both omega fatty acids 3 and 6 as these have been shown to mediate the inflammatory skin response.
Omega 3 fatty acids are increasingly being used to treat irritated skin and show an overall improvement in skin conditions. Eicosatetraenoic acid (EPA), a well-known omega 3, which works by preventing the synthesis of another omega metabolite known as arachidonic acid. Arachidonic acid is an omega 6, making it pro-inflammatory. Low levels of omega 6 fatty acids promote inflammation of the skin, which in turn reduces overall appearance and health.
 Total Pooch Dog Supplements, Tear Stain Removers, De-wormers, Tylosin for Dogs and other great products.
Total Pooch Dog Supplements, Tear Stain Removers, De-wormers, Tylosin for Dogs and other great products.



